tyrannosaurus
Mar 10, 2020
VOSIM oscillator for the ‘Logue platform
Description
Original Werner Kaegi’s paper describes sound synthesis technique which is called VOSIM (for VOice SIMulation). It’s an algorithm which is used in speech synthesis to generate vowels (but it could be used for the fricative consonants or whole syllables as stated in paper). This method is fairly simple and well fitted to be implemented as ‘Logue oscillator. Other methods like e.g. FOF or formant synthesis are more complex in implementation or harder computationally.
Sound examples
Binaries
Only NTS-1 unit was tested on real hardware by me.
If you use this oscillator and you like it — please donate: PayPal
Code
Follow the instructions in README.md to compile oscillators if you want to do it manually. Feel free to modify the code, it’s easy and fun.
Parameters explanation
| param | logue param | closest term in Kaegi paper |
|---|---|---|
M |
shape | delay |
b |
shift-shape | attenuation |
Freq |
param1 | reciprocal of pulse T multiplied by 1 - M |
N |
param2 | number of pulses per period |
LFO Target |
param3 | LFO Target: 1 means delay, 2 means attenuation |
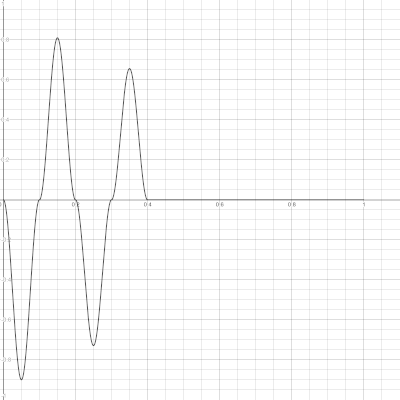
To understand these parameters better read Kaegi’s paper and consider the graphs below: one oscillator cycle is shown on the graphs.
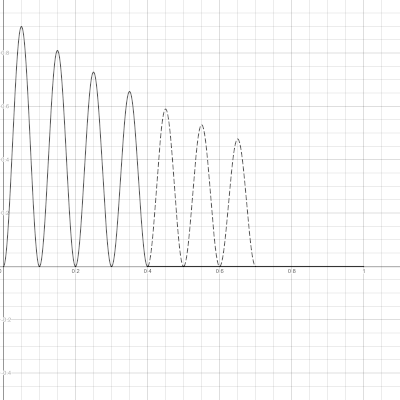
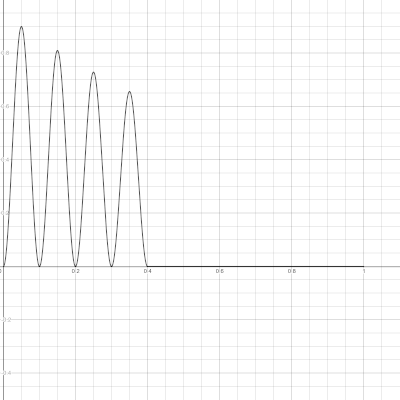
Params are:
- delay
M = 0.3 - attenuation
b = 0.9 - pulse width
T = 0.1 - number of pulses
N = 4
Since clever trick used in ‘Logue SDK always maps phase to [0.0, 1.0) interval we can calculate the Freq param with the formula
Freq = (1.0 - M) ÷ T
So Freq = (1.0 - 0.3) ÷ 0.1 = 7
Current implementation allows negative values of attenuation b so waveform will look like on the figure below